An allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule.
Allylic vs vinylic hydrogen.
The name is derived from the latin word for garlic allium sativum in 1844 theodor wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it schwefelallyl.
An allylic hydrogen is a hydrogen atom that is bonded to an allylic carbon in an organic molecule.
Allyl group holds three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms on the other hand vinyl group has two carbon atoms and three hydrogen atoms.
Allyl groups have three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms.
Benzylic position allylic position propargylic position aryl aryl hydrogen.
Identify the number of allylic and vinylic hydrogens in the pictured molecules.
A hydrogen atom bonded to an sp 2 carbon of an alkene.
The vinylic hydrogens are shown in red.
The allylic carbon is bonded to a carbon atom which is doubly bonded to another carbon atom.
The general formula for allyl is r ch 2 ch ch 2 in which the asterisk carbon atom is an allylic carbon atom.
Key difference allyl vs vinyl both allyl and vinyl groups have slightly similar structures with a small variation.
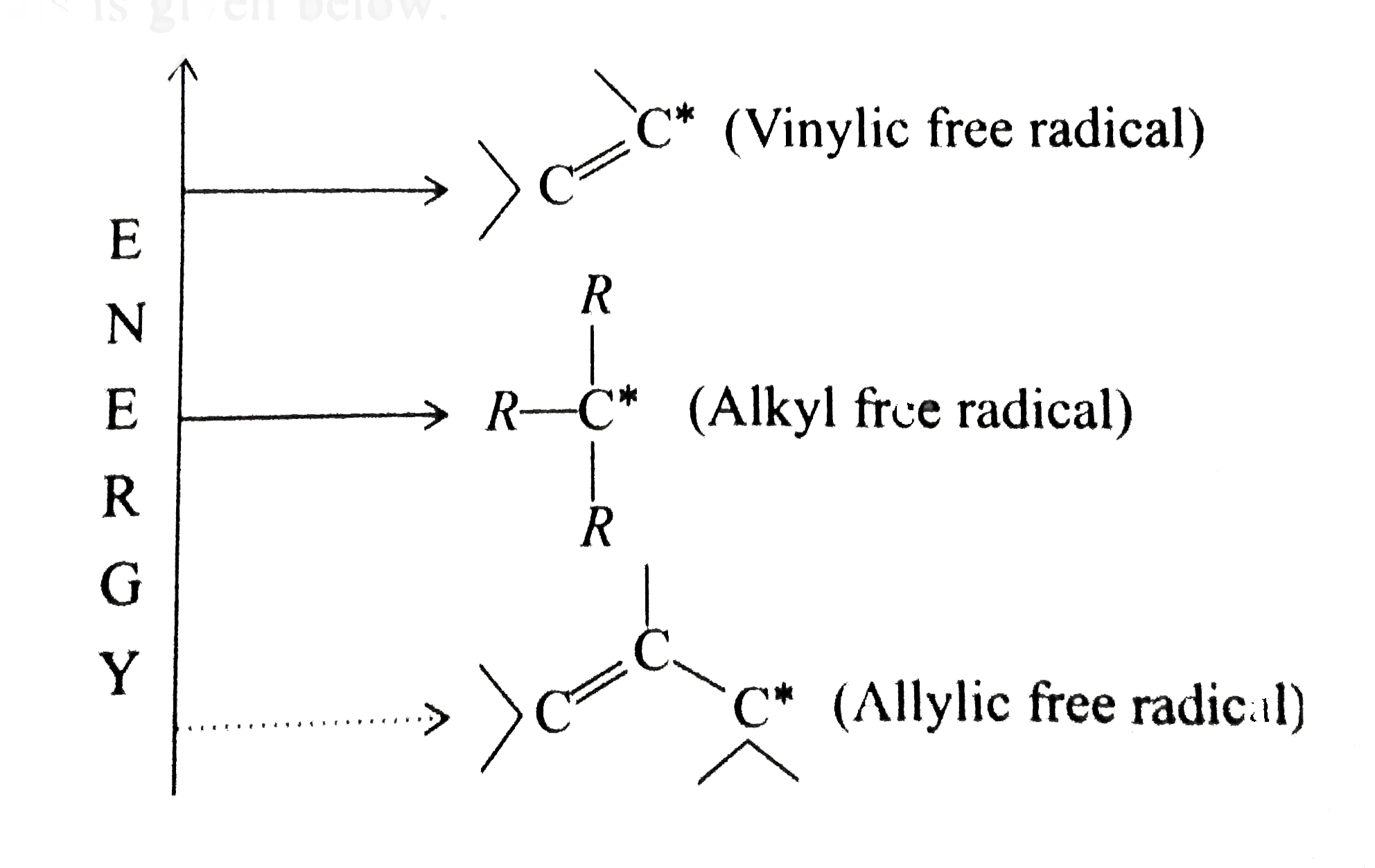
This organic chemistry video tutorial explains how to determine which carbocation is most stable.
It provides plenty of examples including allylic and vinyli.
Allyl form a stable carbocation because of the electron delocalization whereas vinylic carbocations are unstable as they lack p character.
Allyl indicates a functional group with structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule it consists of methylene bridge ch 2 in between the vinyl group ch ch 2 and the rest of the molecule therefore allyl group contains sp 2 hybridized vinyl carbon atoms and sp 3 hybridized allyl carbon atom.
The allylic carbon atom is more reactive than normal.
Both groups own a double bond between two carbon atoms where all the other atoms are bonded through single bonds.
The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon.
The key difference between these two structural components is the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
None of the other hydrogens are vinylic.